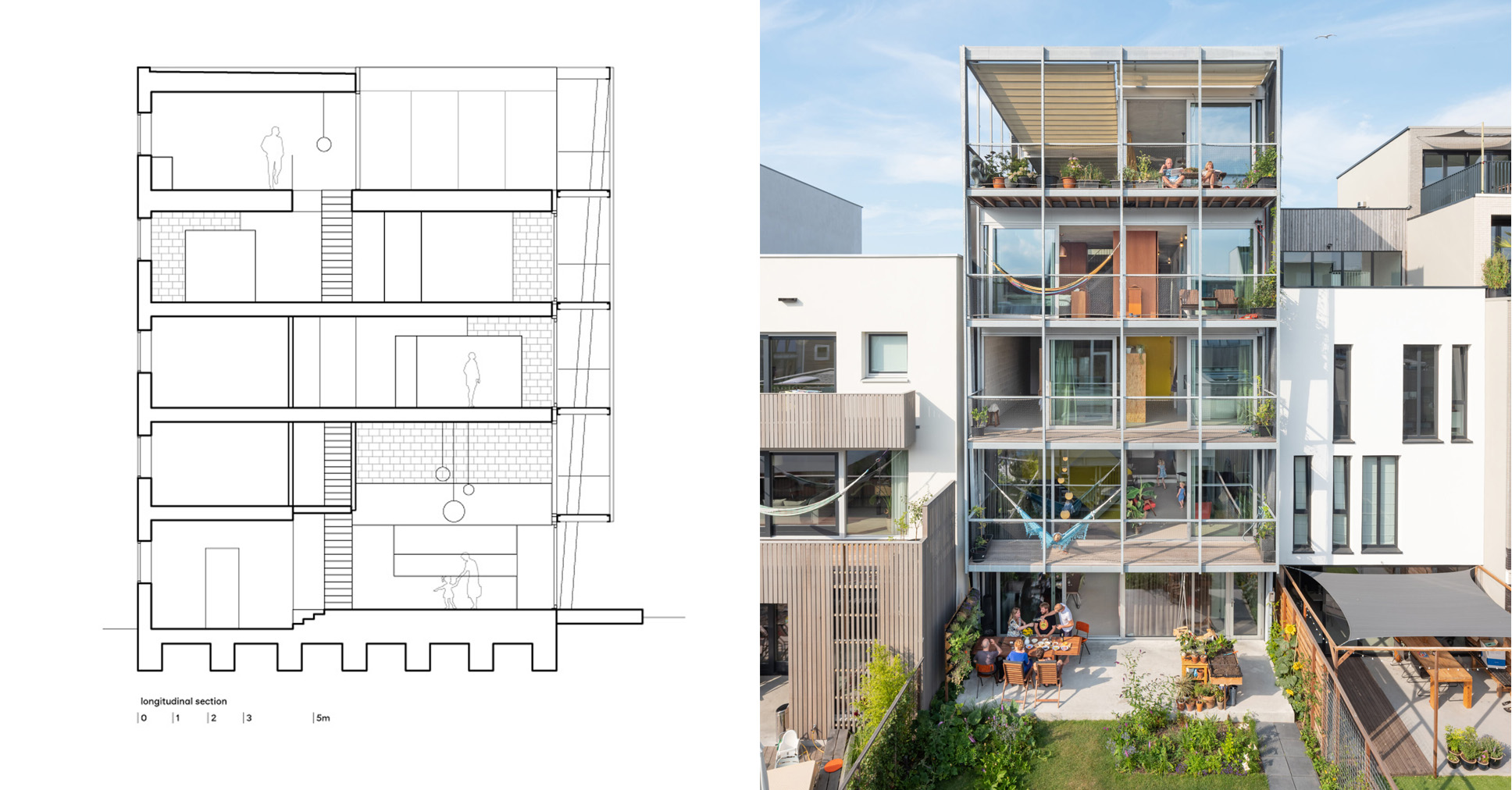
The Future of Urban Development in Mongolia: Insights from the Hunnu City Design Competition

 Alex Millet via Shutterstock
Alex Millet via Shutterstock
Mongolia, the world's second-largest landlocked country, spans 1.5 million square kilometers. Yet, over 50% of its population—approximately 1.7 million people—reside in Ulaanbaatar, a city that occupies just 0.3% of the nation's total land area. This disproportionate population concentration has led to significant regional development imbalances and mounting urban challenges in the capital.
In response to these issues, Ulaanbaatar has undergone a series of comprehensive urban development initiatives. Since the first master plan was introduced in 1954, six such plans have been created. The latest, the Ulaanbaatar 2040 Master Plan, includes a strategic vision to decentralize urban growth through the development of two new satellite cities—one of which is the Hunnu City project.