North Macedonia Pavilion at the Venice Architecture Biennale Revisits the Brutalist Architecture of Skopje
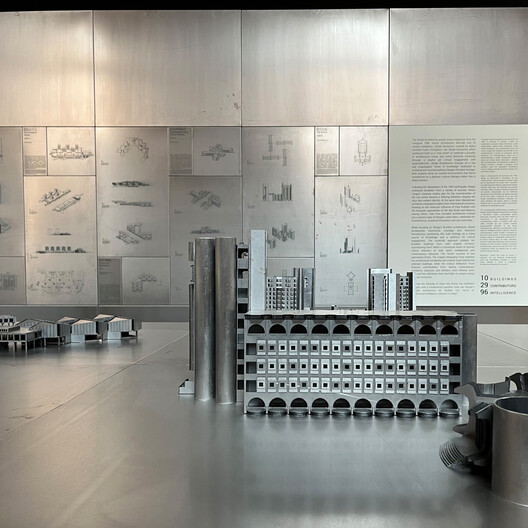

 Strada Brutalissima. Pavilion of the Republic of North Macedonia at the 19th Venice Architecture Biennale, 2025. Image Courtesy of Blagoja Bajkovski
Strada Brutalissima. Pavilion of the Republic of North Macedonia at the 19th Venice Architecture Biennale, 2025. Image Courtesy of Blagoja Bajkovski
The Republic of North Macedonia Pavilion at the 19th Venice Architecture Biennale is dedicated to the Brutalist architecture of its capital city, Skopje. This architectural movement has given the city a distinctive identity following the earthquake that struck in 1963. According to pavilion curator, architect Blagoja Bajkovski, in the aftermath of the disaster, Skopje embraced Brutalism from a variety of sources. One of the most prominent of these was Kenzo Tange's reconstruction plan, developed after an international competition organized by the United Nations in 1965. The exhibition, titled Strada Brutalissima, recounts this identity, the events that shaped it, and the buildings that continue to represent it through a series of architectural models. Inspired by the 1980 Venice Architecture Biennale's Strada Novissima, the project reinterprets the concept of a curated "street," this time centered on Skopje's Brutalist heritage.