10 Facts About Centre Pompidou, a High-Tech Architectural Icon in Paris

Got a project that’s too contemporary for your client? Submit your conceptual works, images and ideas for global recognition and print publication in the 2025 Vision Awards! The clock is ticking — submit your work ahead of the Main Entry deadline on June 6th.
After almost fifty years of being open to the public, the Centre Pompidou will temporarily close for a major renovation. The works will address structural aging and bring the facility up to current safety, accessibility and environmental standards, ensuring the Centre Pompidou can continue to operate as a world-class institution. The closure is expected to last approximately five years, with reopening planned for 2030.
As would-be visitors postpone their architectural pilgrimages, it’s an opportune moment to revisit some of its most distinctive architectural features. Since its inauguration in 1977, it is one of Paris’ most recognizable landmarks, an icon of High-Tech architecture and a beacon of cultural innovation. Designed by architects Renzo Piano and Richard Rogers, the building turned traditional museum design upside down (or, rather, inside-out!), with its boldly exposed infrastructure and brightly color-coded mechanical systems.
French architecture firm Moreau Kusunoki, in collaboration with Frida Escobedo Studio, was selected to lead the ambitious project for their thoughtful approach to contemporary interventions in historic settings and their commitment to sustainability. The upgrade involves no expansion of the original structure; instead, it focuses on improving the building’s long-term resilience and functionality while staying true to the original design’s spirit.
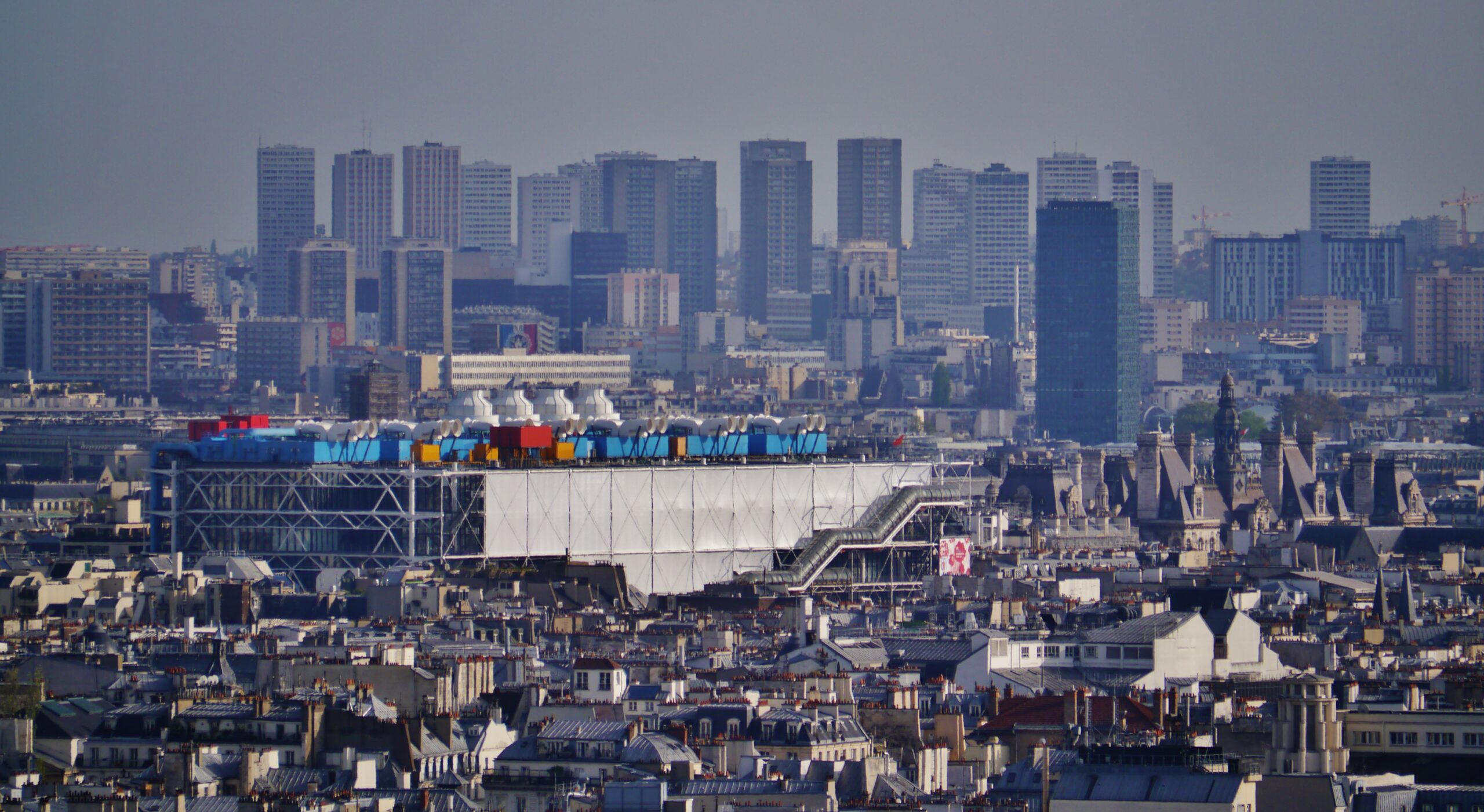

View of Centre Pompidou from Montmartre, Paris, France. | Photo by Zairon via Wikimedia Commons under CC BY-SA 4.0.
1. The Centre Pompidou is undoubtedly a bold architectural landmark and a prime example of High-Tech Architecture, also known as Structural Expressionism. This style emerged in the late 1960s, primarily in the United Kingdom, and later spread internationally. Highly influenced by Modernism and Brutalism, High-Tech Architecture proudly displays building components, such as structural and mechanical systems, which are typically concealed. The style also celebrates industrial materials, engineering innovation, and prefabrication.
Renzo Piano and Richard Rogers were part of a wave of architects, including Norman Foster, Santiago Calatrava, Nicholas Grimshaw, and Michael Hopkins, among others, who contributed significantly to the style’s development. As one of the style’s earliest and most provocative designs, the Centre Pompidou remains an all-time architectural icon.
2. The Centre Pompidou opened its doors in 1977, stirring controversy because of its industrial, rough aesthetic. Its boldly displayed structural and mechanical systems made the building look more like an industrial construction — such as factories or power plants — than a conventional civic building. Many critics saw it as out of place in historic Paris, especially compared to institutions like the Louvre, which embody traditional architectural principles. Yet, its provocative aesthetics, once criticized, are now recognized as a strength, pushing the boundaries of what an art institution can look like. Today, the Centre Pompidou is a powerful symbol of contemporary architecture that reflects the spirit of artistic avant-garde.
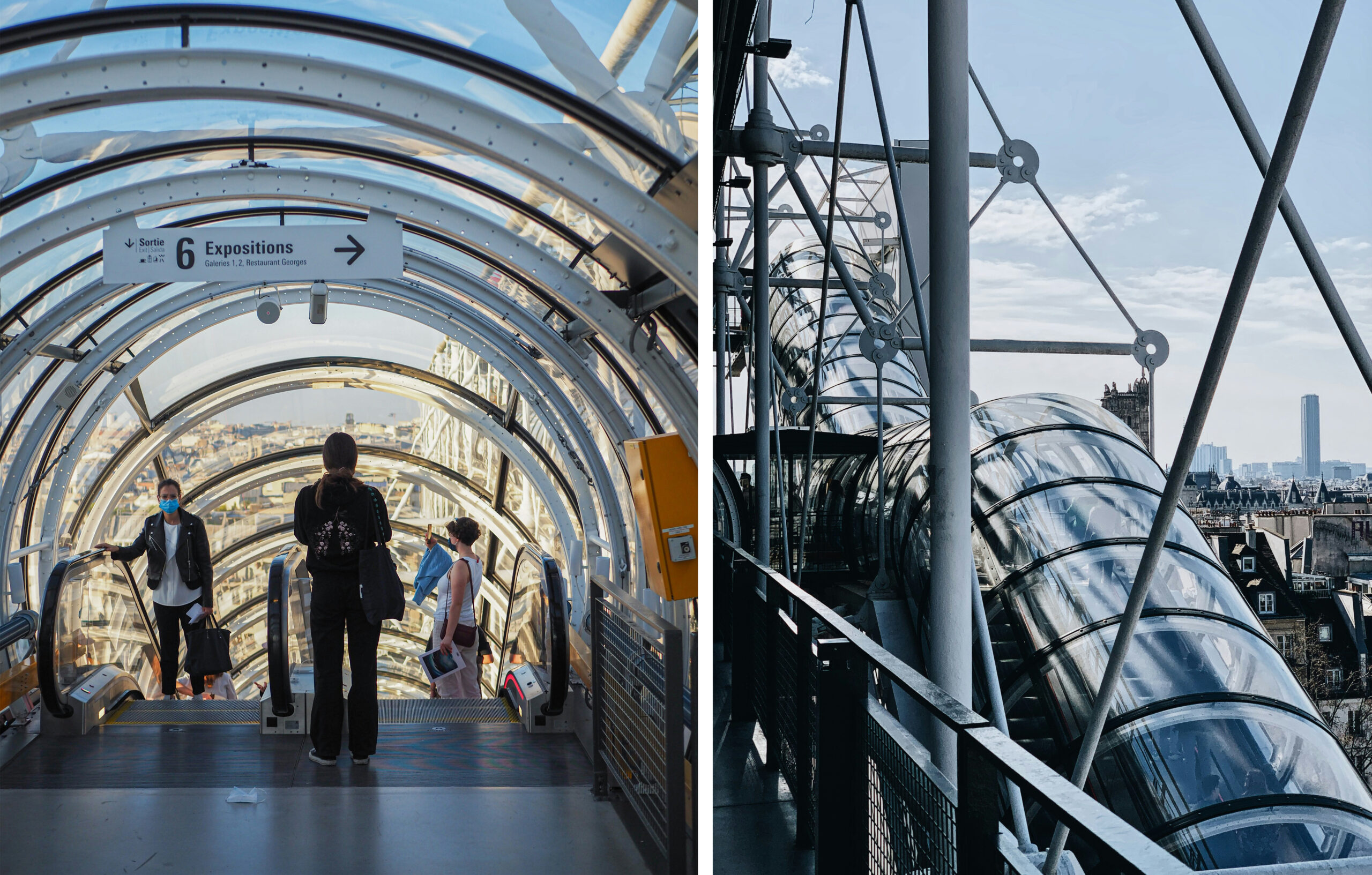

Views of Paris from Centre Pompidou’s panoramic escalator. Photos by Huân Lê via Unsplash (right) and Florian Peeters via Unsplash (left).
3. Located in the Beaubourg area of Paris’ Marais district, the Centre Pompidou — also referred to as Beaubourg — has played a key role in revitalizing the neighborhood and activating public life with its plaza. It represents far more than a traditional museum, promoting street performances and cultural events. This strategy has transformed the area into a dynamic neighborhood, attracting both locals and visitors.
4. The Centre Pompidou was envisioned as a multidisciplinary cultural institution. In addition to its world-class modern and contemporary art collection, it also houses the Bibliothèque publique d’information (Bpi), the Institute for Research and Coordination in Acoustics/Music (IRCAM), movie theaters, and performance spaces. The integration of multiple disciplines under one roof promotes a vibrant cultural ecosystem that engages a broad and diverse public.
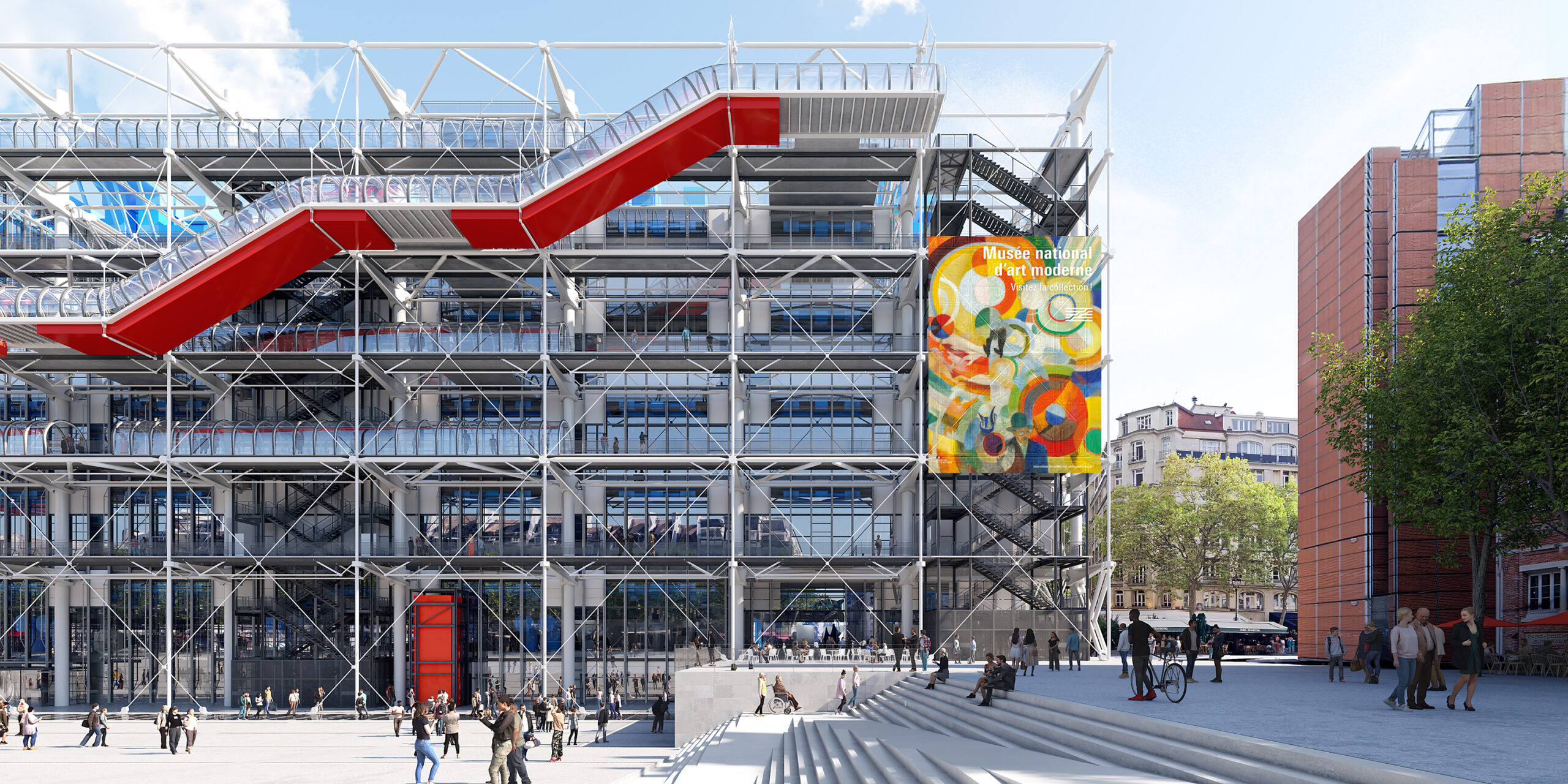
5. One of the Centre Pompidou’s most striking features is the external glass-enclosed escalator that rises the south façade overlooking the plaza. Nicknamed “la chenille” — French for “the caterpillar” — the escalator is more than just functional; it is a defining part of the visitor experience, offering panoramic views of Paris. This façade, with its distinctive escalator, has become so emblematic that a stylized drawing of it serves as the Centre Pompidou’s logo and branding.
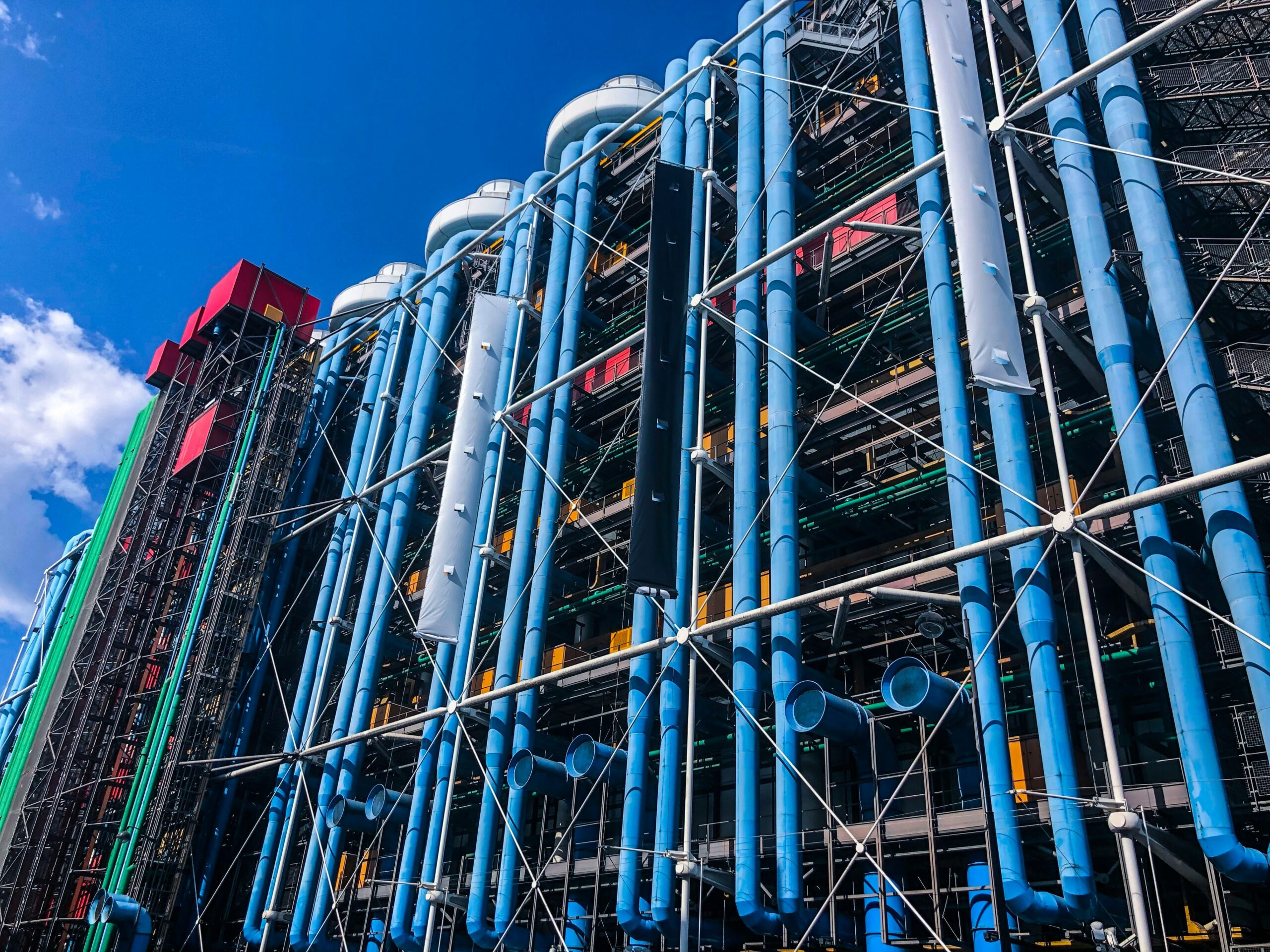

Centre Pompidou’s color-coded infrastructure. | Photo by Adora Goodenough via Unsplash.
6. Another outstanding feature of the building’s design is its color-coded infrastructure systems, which not only serves a functional purpose but also creates a vibrant visual language. Each system is painted a different color to indicate its function:
- Blue for air ducts
- Green for plumbing
- Yellow for electrical systems
- Red for circulation (staircases, escalators, and elevators)
The upcoming upgrade project will maintain this defining design aspect — so closely tied to the building’s identity and the spirit of the institution it houses — while improving the building’s overall functionality and sustainability with more energy-efficient technologies.
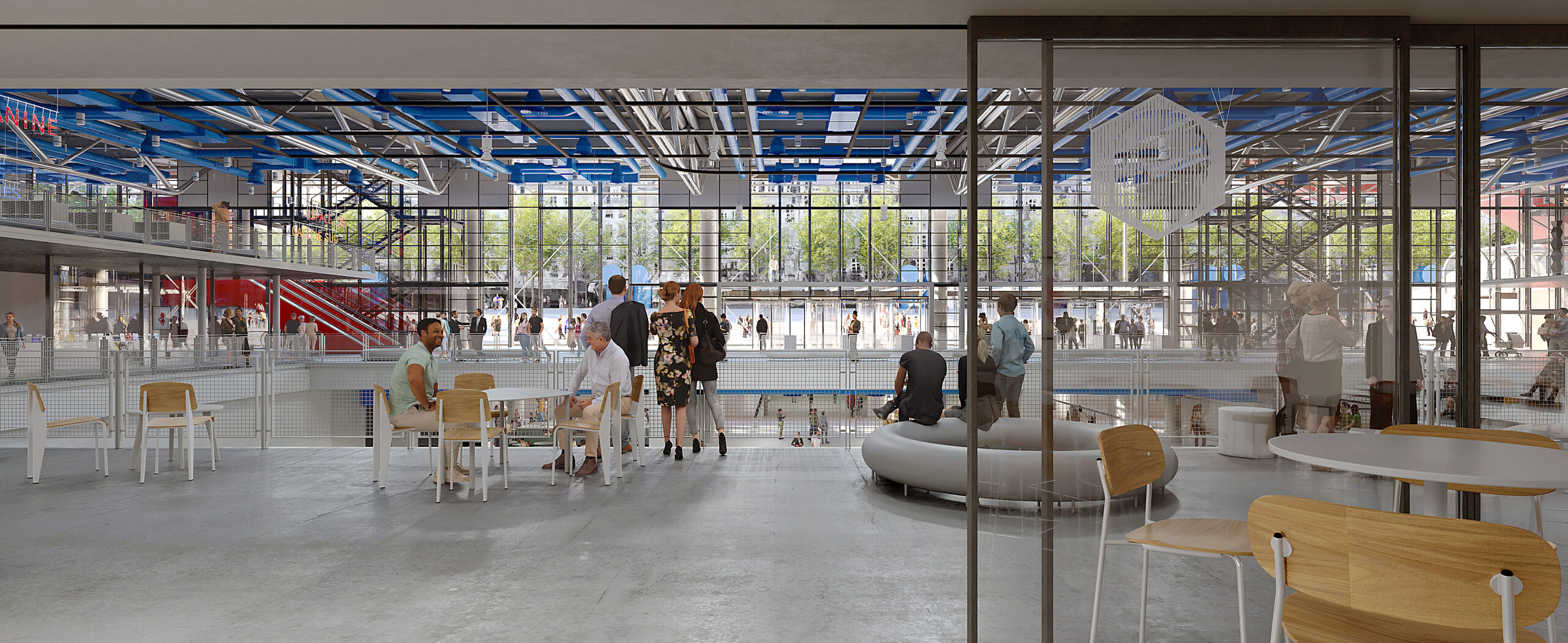

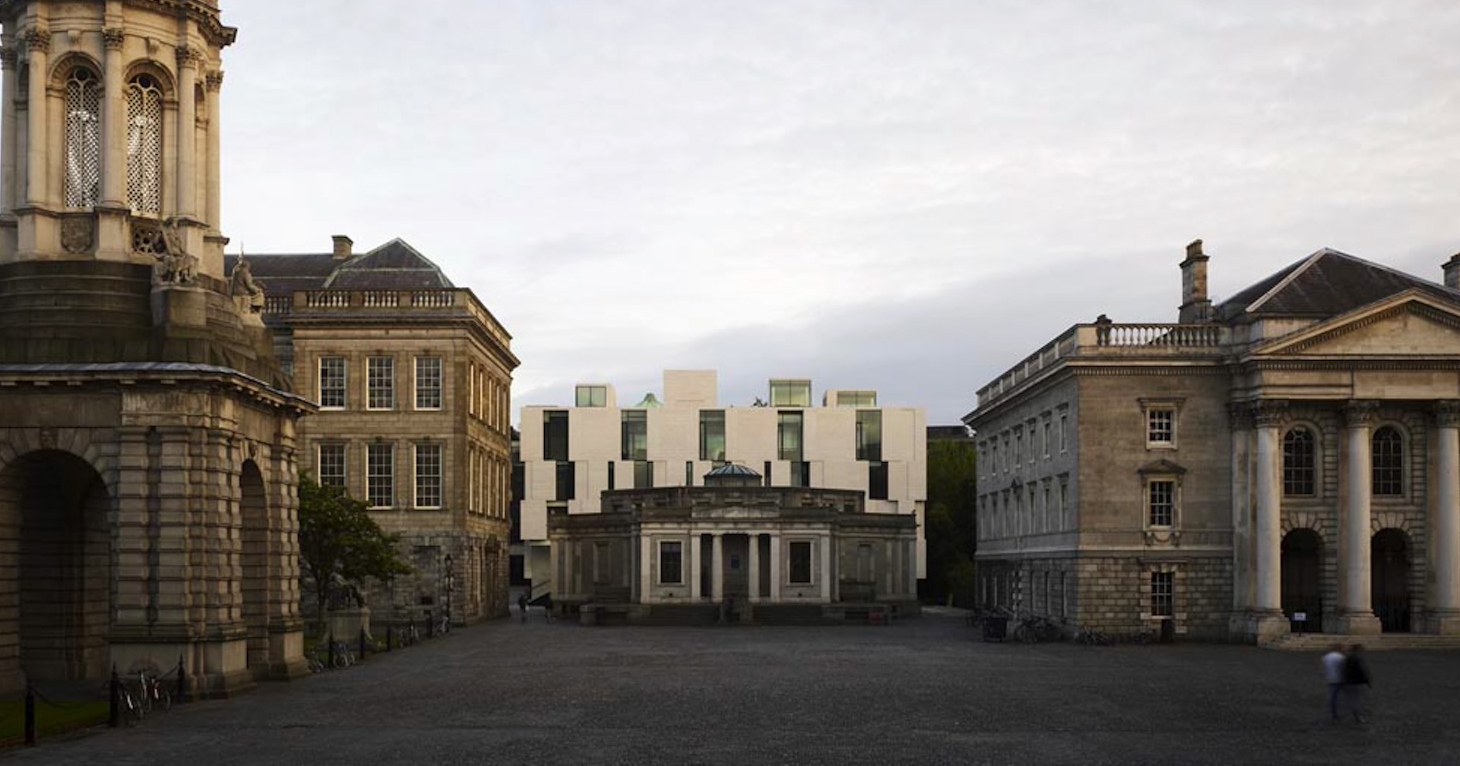
Centre Pompidou 2030 design by Moreau Kusunoki in association with Frida Escobedo Studio. Paris, France | Visualization by Moreau Kusunoki
7. Like the building’s infrastructure systems, the structure is also external, forming a steel exoskeleton composed of prefabricated steel trusses and diagonal bracing. This design approach reflects Renzo Piano and Richard Rogers’ intent to create a visually striking architecture that emphasizes clarity and legibility. The renovation will preserve and restore this architectural expression while making significant upgrades to meet today’s standards, including the refurbishment of the steel frame and façades without compromising the original design intent.
8. By placing the building’s structural and mechanical systems on the exterior, the Centre Pompidou offers expansive open spaces that can be easily reconfigured. This design approach optimizes the flexible use of spaces, ideal for exhibitions and performances. The new design will not expand the original structure but will make better use of previously underutilized areas. According to the architect’s project statement, the renovation seeks to “rationalize and simplify the spatial organization in order to establish clear, readable layout principles.”
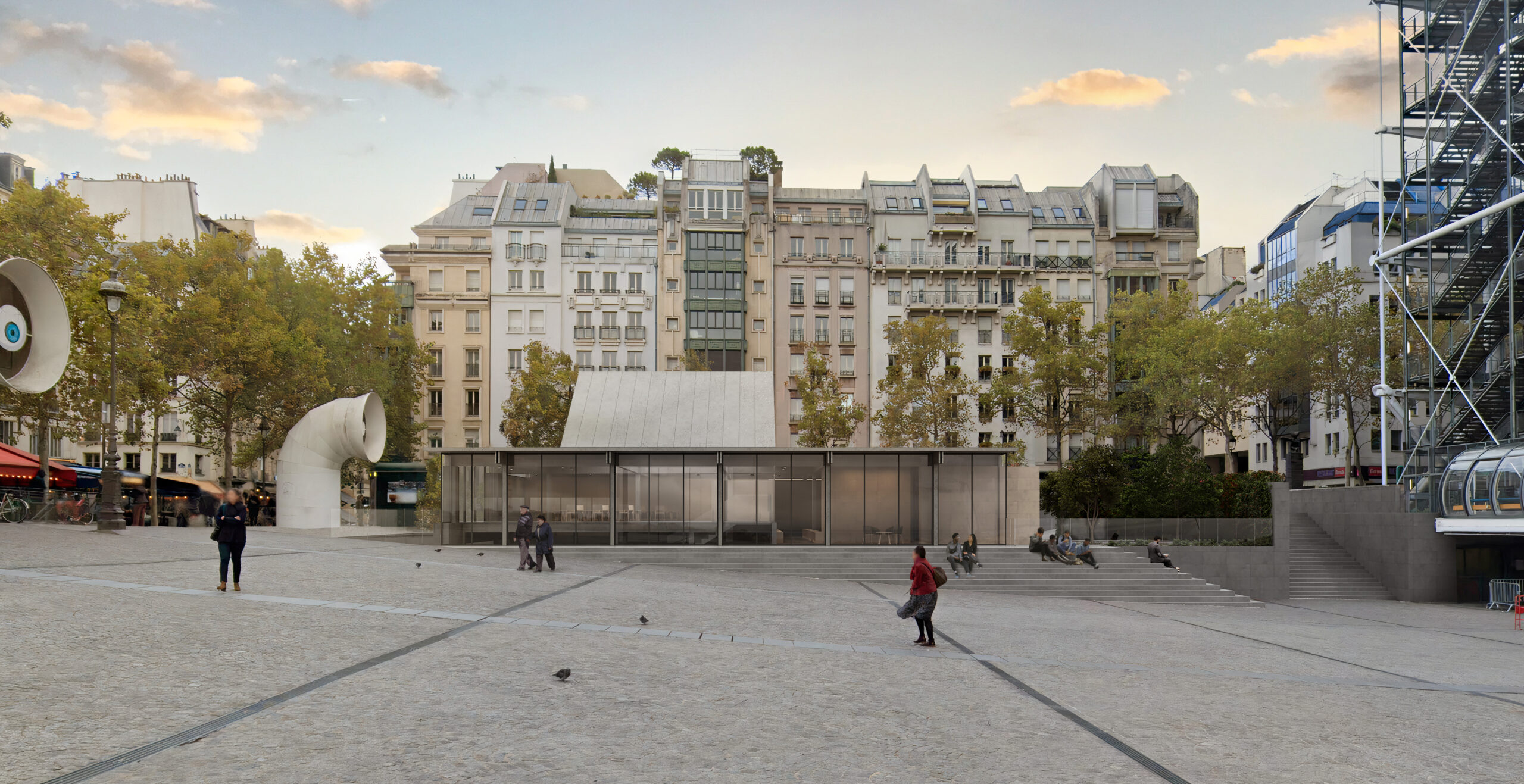

Centre Pompidou 2030 design by Moreau Kusunoki in association with Frida Escobedo Studio. Paris, France | Visualization by Moreau Kusunoki
9. In their project statement, Moreau Kusunoki also explain the shift in societal values since the Centre Pompidou opened in 1977: “When the Centre Pompidou was conceived, notions of speed, animation and information dissemination symbolized progress. Today, the paradigm is reversed: faced with information overload, fragmented attention and isolation caused by screen time, the Centre Pompidou offers a space where mediation, human interaction and the physical experience are central.”
10. The Atelier Brancusi is integral to the Pompidou’s identity. Situated just beside the main building on Place Georges-Pompidou, it will also close temporarily during the renovation. The renovation measures are aimed to ensure its careful preservation and eventual reopening in 2030.
Got a project that’s too contemporary for your client? Submit your conceptual works, images and ideas for global recognition and print publication in the 2025 Vision Awards! The clock is ticking — submit your work ahead of the Main Entry deadline on June 6th.
Top image: Centre Pompidou 2030 by MOREAU KUSUNOKI,Paris,France
The post 10 Facts About Centre Pompidou, a High-Tech Architectural Icon in Paris appeared first on Journal.