Who Owns Public Space? Three Active Models of Shared Management Shaping Urban Commons in Europe and New York

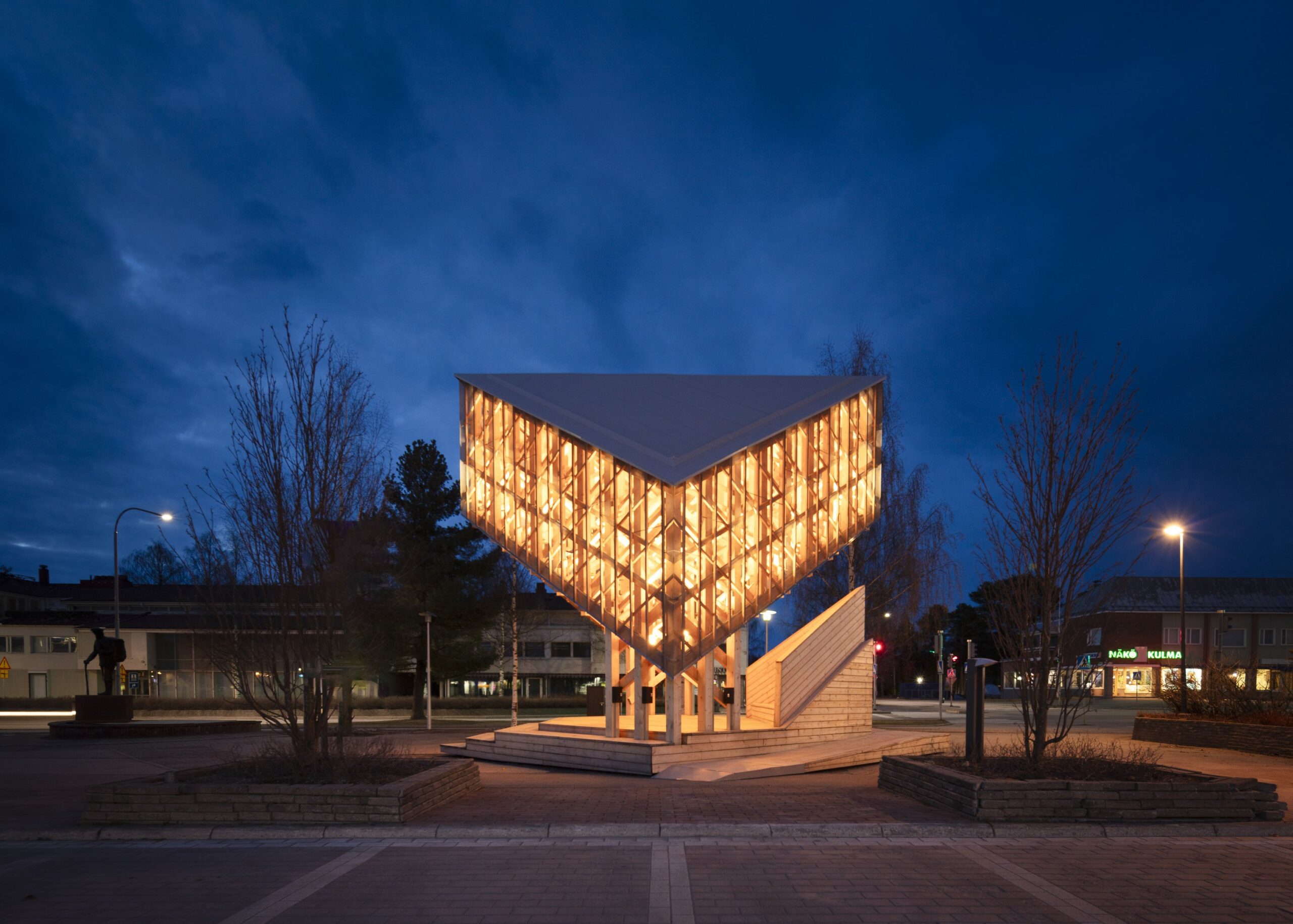
 The Common Corner at Morris Houses, a New York Public Housing Development, in Bronx, NY. Image © Brook Banister
The Common Corner at Morris Houses, a New York Public Housing Development, in Bronx, NY. Image © Brook Banister
Public space is often understood as belonging to no one in particular, collectively accessible yet institutionally maintained, yet a growing number of initiatives are challenging this assumption by testing shared management and distributed ownership models. In Paris, Adoptez un banc introduces a sponsorship-based approach, allowing individuals and groups to support temporarily and symbolically claim responsibility for historic public furniture without compromising its collective use. Elsewhere in the city, community gardens operating under the Main Verte framework demonstrate a self-managed model, in which public and private landowners retain ownership while delegating day-to-day control to citizen associations for food production and shared use. In New York, The Common Corner represents a third pathway, based on institutional collaboration and participatory design, where public agencies, nonprofits, designers, and residents co-produce public space within a public housing context. Taken together, these three cases suggest that care, authorship, and responsibility can be distributed across citizens and institutions, producing more resilient, locally grounded urban environments.